Scammers, cyber thieves, and NFT hackers commonly target NFT projects, platforms, and owners across different platforms. Scammers infiltrate NFT communities and constantly hack online NFT websites or platforms by stealing away worthy NFTs. Such scammers then sell the stolen NFTs on secondary markets for thousands of dollars. The recent breaches into multiple NFT platforms and websites have common security vulnerabilities that have led to the loss of many expensive NFT and crypto assets.
Suppose you believe your NFT assets are secure because you know all the typical NFT scams and can easily avoid them. With that said, you may want to reevaluate your understanding of NFT security, as these scammers constantly use new tactics and strategies to trick users of various NFT communities, including Twitter and Discord.
Despite the present bear market for NFT assets compared to the significantly booming NFT market of 2021, NFT scams are on the rise in 2022, accounting for 20 million worth of NFTs, according to a report by blockchain analysis and crypto compliance company, Elliptic.
Furthermore, the report claims that, on average, NFT scammers could obtain $300,000 per scam in 2022, with 23% of scams happening because of NFT phishing attempts on social media platforms. The actual scope of similar NFT scams is probably far larger because not all users publicly report such offenses.
It's become increasingly necessary to exercise extreme vigilance and avoid any NFT scams. A thorough grasp of every NFT scam or cyberattack will enable you to remain aware of the most recent vulnerabilities in the NFT community. Please stick with us to the end of this article to learn about one of the most prevalent NFT scam of 2022, plaguing NFT Twitter communities at an alarming rate.
As part of our 'Common NFT Scam' series, this article will cover one of the most cunning NFT phishing scam on Twitter, Discord, and other NFT community platforms, commonly known as the Unicode Letters phishing hack. It will discuss best practices and strategies to avoid the Unicode Letters NFT phishing hack.
Use of Unicode Letters for NFT Phishing Scams:
Phishing is as rampant as ever, but now scammers are using new strategies to defraud NFT owners and steal their assets. By tricking users into clicking on URL links with Unicode Letters on Twitter and other NFT platforms, scammers get access to their NFT wallets and steal away their expensive NFTs from their wallets.
Unicode Letter Scams are the latest NFT scams on NFT communities and platforms such as Twitter. As the term implies, the Unicode Letter scam involves tricking individuals by spoofing URLs with Unicode characters that resemble actual letters. This URL leads to fake websites that, once again, mimic the original versions. Such NFT crypto scams target novices or NFT owners with less expensive NFTs.
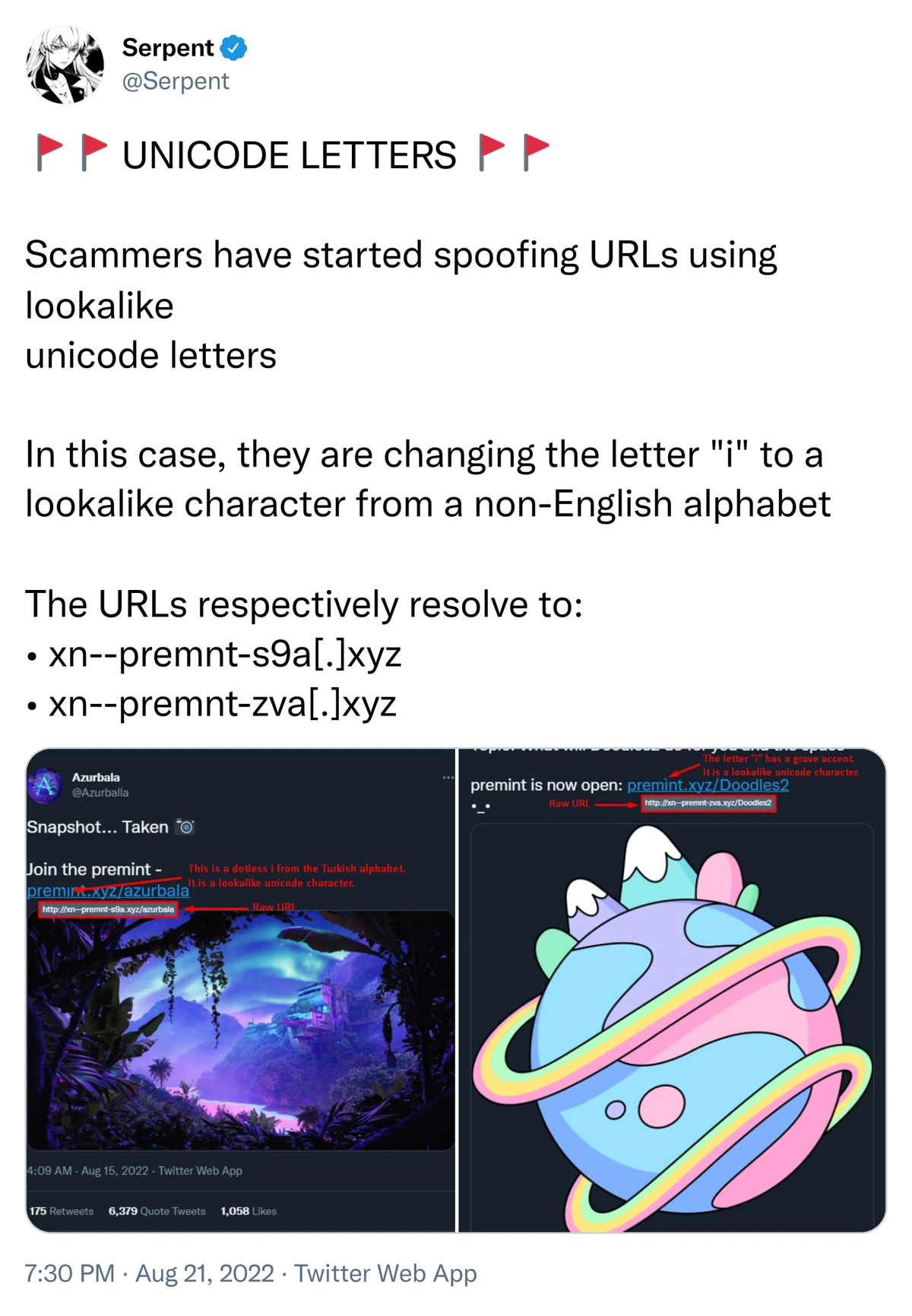
Source: Web3 Security Analyst Serpent
Many online programs and services allow anyone to build malicious URLs by replacing original characters with Unicode letters. These Unicode letter URLs occasionally redirect to another hyperlink for concealing specific domain names.
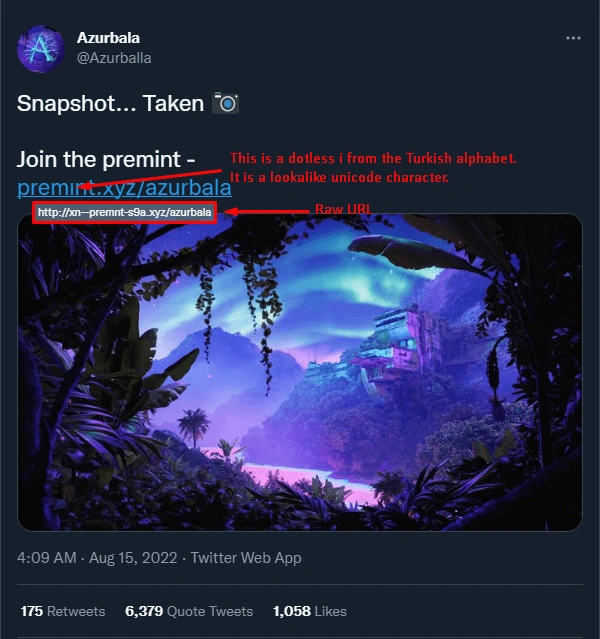
The following are examples of Unicode letters. Serpent shared these samples in his tweet about the Unicode Letter scam, so they brilliantly demonstrated the NFT scam.
Unicode Letters URL NFT Scam | Source: Web3 Security Analyst Serpent
In the above example, the counterfeit premint link uses the Unicode Turkish character instead of the letter i. Like other phishing scams, when an NFT owner clicks the link, the phishing website redirects the victim to the identical website as a @PREMINT NFT and prepays the scammers with counterfeit NFTs.
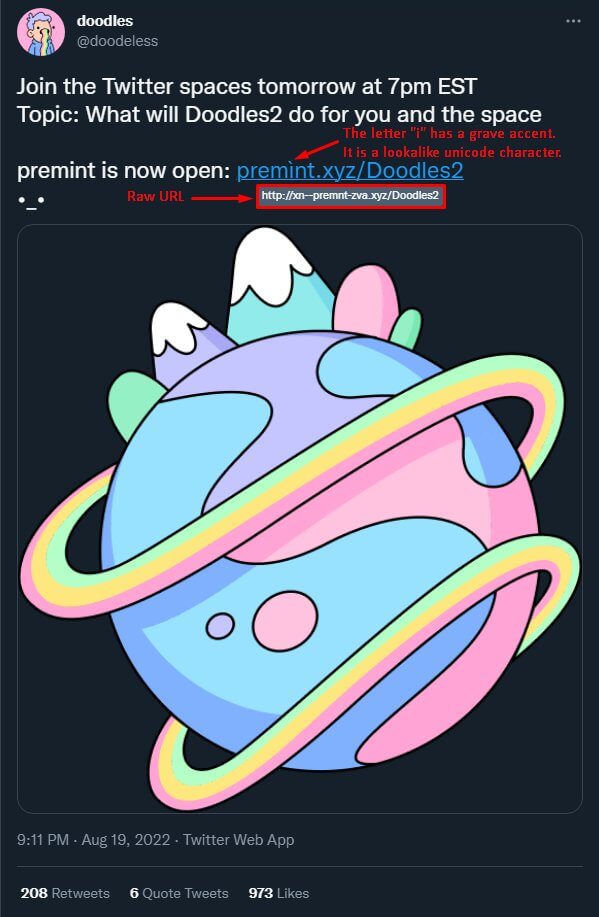
Here is another example of the Unicode Letter NFT phishing scam:
Unicode Letters URL NFT Scam | Source: Web3 Security Analyst Serpent
How does the Unicode Letters NFT Phishing Scam work?
The Unicode Protocol is an alternative to traditional character codes, which lack computer code representation for every letter, number, or other technical expertise in all languages. The Unicode protocol assigns a unique computer code to each character known to humans, regardless of its language, platform, or device.
You're probably wondering what it all has to do with NFT hacks. It's not the Unicode but the Unicode domain or URL that is the problem.
A universal resource locator, or 'URL,' is defined as a complete online address that links a DNS to a specific website. The domain name of any website represents its URL to the everyday user—for example, Google.com, NotCommon.com, etc.
Historically, web engineers only limited online domain names and URLs to ASCII characters. This was because the internet’s primary development happened in the United States and initially employed only ASCII characters, representing English language characters such as letters, numerals, etc. This was vital for the integrity and safety of URLs because it ensured the uniformity of computer code representation worldwide.
Web standards evolved as the World Wide Web became increasingly global. You can now write web addresses in any language thanks to a standard developed in 2003 that allows for the use of nearly all Unicode characters. These Internationalized domain names (IDNs) posed new issues for IT security experts and companies around the world regarding visual spoofing, the practice of manipulating international language characters to make a scam or phishing URL appear visually authentic.
How to Keep your NFTs Secure from Unicode Letters Scam?
The only way to secure your NFTs by avoiding the Unicode Letters phishing scam is to be highly vigilant and observant when clicking on NFT website links available on Twitter or other social media platforms. Suppose you see any news on Twitter regarding an NFT giveaway, airdrop, or premint. In that case, the first step should always be to confirm the Twitter account and then visit the official website of the NFT project rather than clicking on any external link. The rule of thumb here is your observance, research, and vigilance.
Suppose you see a tweet posting Unicode Letters URLs and impersonating an NFT project. In that case, you should immediately report the user to Twitter and the NFT project team to effectively stop the scam.
The Takeaway
NFT scammers commonly use Unicode Letters URLs for phishing tactics these days to scam NFT owners on a Discord, Twitter, or other social media platform.
Fortunately, most browsers will notify you if you are on any such URLs and show them as Punycode. Punycode is a technique for translating Unicode into the constrained ASCII character subset required for internet network addresses. IDNs that use Punycode as their encoding start with the prefix "xn—" to denote the beginning of a label.
If you use the official NFT websites and platforms or pay close attention to such links on social media platforms, including Twitter, you will remain safe from such scams.
To learn more about NFT scams and security, visit all of our articles.